Glossary
Selected key terms pertaining to medical device development are listed below with References.
Key Terms
There are currently 14 key terms in this directory beginning with the letter A.
abnormal use
conscious, intentional act or intentional omission of an act that is counter to or violates normal use and is also beyond any further reasonable means of user interface-related risk control by the manufacturer
Examples: Reckless use or sabotage or intentional disregard of information for safety are such acts.
Note 1: An intended but erroneous action that is not abnormal use is considered a type of use error.
Note 2: Abnormal use does not relieve the manufacturer from considering non-user interface-related means of risk control.
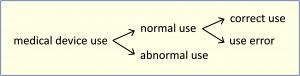
Note 3: The figure below shows the relationships of the types of use.
Examples: Reckless use or sabotage or intentional disregard of information for safety are such acts.
Note 1: An intended but erroneous action that is not abnormal use is considered a type of use error.
Note 2: Abnormal use does not relieve the manufacturer from considering non-user interface-related means of risk control.
Note 3: The figure below shows the relationships of the types of use.

[IEC 62366-1:2015]
accessory
a finished device that is intended to support, supplement, and/or augment the performance of one or more parent devices
[FDA guidance: Medical Device Accessories...(2017)]
accessory
additional part for use with equipment in order to:
– achieve the intended use,
– adapt it to some special use,
– facilitate its use,
– enhance its performance, or
– enable its functions to be integrated with those of other equipment
– achieve the intended use,
– adapt it to some special use,
– facilitate its use,
– enhance its performance, or
– enable its functions to be integrated with those of other equipment
[IEC 60601-1:2012]
accessory for a medical device
an article which, whilst not being itself a medical device, is intended by its manufacturer to be used together with one or several particular medical device(s) to specifically enable the medical device(s) to be used in accordance with its/their intended purpose(s) or to specifically and directly assist the medical functionality of the medical device(s) in terms of its/their intended purpose(s)
[EU MDR 2017/745]
accessory for an in vitro diagnostic medical device
an article which, whilst not being itself an in vitro diagnostic medical device, is intended by its manufacturer to be used together with one or several particular in vitro diagnostic medical device(s) to specifically enable the in vitro diagnostic medical device(s) to be used in accordance with its/their intended purpose(s) or to specifically and directly assist the medical functionality of the in vitro diagnostic medical device(s) in terms of its/their intended purpose(s)
[EU IVDR 2017/746]
accompanying documentation
materials accompanying a medical device and containing information for the user or those accountable for the installation, use, maintenance, decommissioning and disposal of the medical device, particularly regarding safe use
Note 1: The accompanying documentation can consist of the instructions for use, technical description, installation manual, quick reference guide, etc.
Note 2: Accompanying documentation is not necessarily a written or printed document but could involve auditory, visual, or tactile materials and multiple media types.
Note 1: The accompanying documentation can consist of the instructions for use, technical description, installation manual, quick reference guide, etc.
Note 2: Accompanying documentation is not necessarily a written or printed document but could involve auditory, visual, or tactile materials and multiple media types.
[ISO 14971:2019]
active device
any device, the operation of which depends on a source of energy other than that generated by the human body for that purpose, or by gravity, and which acts by changing the density of or converting that energy. Devices intended to transmit energy, substances or other elements between an active device and the patient, without any significant change, shall not be deemed to be active devices
Note: Software shall also be deemed to be an active device
Note: Software shall also be deemed to be an active device
[EU MDR 2017/745]
adulterated drugs and devices
[paraphrased] A drug or device shall be deemed to be adulterated...if
(a) Poisonous, insanitary, etc., ingredients; adequate controls in manufacture...
(b) Strength, quality, or purity differing from official compendium...
(c) Misrepresentation of strength, etc., where drug is unrecognized in compendium...
(d) Mixture with or substitution of another substance...
(e) Devices not in conformity with performance standards...
(f) Certain class III devices...
(g) Banned devices...
(h) Manufacture, packing, storage, or installation of device not in conformity with applicable requirements or conditions...
(i) Failure to comply with requirements under which device was exempted for investigational use...
(j) Delayed, denied, or limited inspection; refusal to permit entry or inspection...
Note: Actual definition is too long to list here.
(a) Poisonous, insanitary, etc., ingredients; adequate controls in manufacture...
(b) Strength, quality, or purity differing from official compendium...
(c) Misrepresentation of strength, etc., where drug is unrecognized in compendium...
(d) Mixture with or substitution of another substance...
(e) Devices not in conformity with performance standards...
(f) Certain class III devices...
(g) Banned devices...
(h) Manufacture, packing, storage, or installation of device not in conformity with applicable requirements or conditions...
(i) Failure to comply with requirements under which device was exempted for investigational use...
(j) Delayed, denied, or limited inspection; refusal to permit entry or inspection...
[OLRC 21USC9 section 351 excerpt]
Note: Actual definition is too long to list here.
amortization
an accounting technique used to periodically lower the book value of a loan or intangible asset over a set period of time
Note: The term "amortization" can refer to two situations. First, amortization is used in the process of paying off debt through regular principal and interest payments over time. An amortization schedule is used to reduce the current balance on a loan, for example a mortgage or car loan, through installment payments. Second, amortization can also refer to the spreading out of capital expenses related to intangible assets over a specific duration – usually over the asset's useful life – for accounting and tax purposes.
Note: The term "amortization" can refer to two situations. First, amortization is used in the process of paying off debt through regular principal and interest payments over time. An amortization schedule is used to reduce the current balance on a loan, for example a mortgage or car loan, through installment payments. Second, amortization can also refer to the spreading out of capital expenses related to intangible assets over a specific duration – usually over the asset's useful life – for accounting and tax purposes.
[Investopedia]
analytical performance
ability of an IVD medical device to detect or measure a particular analyte
[ISO 20916:2019]
analytical performance
the ability of a device to correctly detect or measure a particular analyte
[EU IVDR 2017/746]
ARCI chart (RACI chart)
chart describing the participation by various roles when completing tasks and/or deliverables
audit
systematic, independent and documented process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled
Note 1: The fundamental elements of an audit include the determination of the conformity of an object according to a procedure carried out by personnel not being responsible for the object audited.
Note 2: An audit can be an internal audit (first party), or an external audit (second party or third party), and it can be a combined audit or a joint audit.
Note 3: Internal audits, sometimes called first-party audits, are conducted by, or on behalf of, the organization itself for management review and other internal purposes, and can form the basis for an organization’s declaration of conformity. Independence can be demonstrated by the freedom from responsibility for the activity being audited.
Note 4: External audits include those generally called second and third-party audits. Second party audits are conducted by parties having an interest in the organization, such as customers, or by other persons on their behalf. Third-party audits are conducted by external, independent auditing organizations such as those providing certification/registration of conformity or governmental agencies.
Note 1: The fundamental elements of an audit include the determination of the conformity of an object according to a procedure carried out by personnel not being responsible for the object audited.
Note 2: An audit can be an internal audit (first party), or an external audit (second party or third party), and it can be a combined audit or a joint audit.
Note 3: Internal audits, sometimes called first-party audits, are conducted by, or on behalf of, the organization itself for management review and other internal purposes, and can form the basis for an organization’s declaration of conformity. Independence can be demonstrated by the freedom from responsibility for the activity being audited.
Note 4: External audits include those generally called second and third-party audits. Second party audits are conducted by parties having an interest in the organization, such as customers, or by other persons on their behalf. Third-party audits are conducted by external, independent auditing organizations such as those providing certification/registration of conformity or governmental agencies.
[ISO 9000:2015]
Medical device developers are strongly encouraged to consult the listed reference for each key term to fully understand the context behind the definition and its intended application.
Definitions from the FDA Code of Federal Regulation (CFR) are listed without dates and are accurate through December 2020. Consult the listed FDA reference (online) to confirm the latest definition.
