Glossary
Selected key terms pertaining to medical device development are listed below with References.
Key Terms
[EU MDR 2017/745, EU IVDR 2017/746]
[ISO 11139:2018]
(1) Class I means the class of devices that are subject to only the general controls authorized by or under sections 501 (adulteration), 502 (misbranding), 510 (registration), 516 (banned devices), 518 (notification and other remedies), 519 (records and reports), and 520 (general provisions) of the act. A device is in class I if (i) general controls are sufficient to provide reasonable assurance of the safety and effectiveness of the device, or (ii) there is insufficient information from which to determine that general controls are sufficient to provide reasonable assurance of the safety and effectiveness of the device or to establish special controls to provide such assurance, but the device is not life-supporting or life-sustaining or for a use which is of substanial importance in preventing impairment of human health, and which does not present a potential unreasonable risk of illness of injury.
(2) Class II means the class of devices that is or eventually will be subject to special controls. A device is in class II if general controls alone are insufficient to provide reasonable assurance of its safety and effectiveness and there is sufficient information to establish special controls, including the promulgation of performance standards, postmarket surveillance, patient registries, development and dissemination of guidance documents (including guidance on the submission of clinical data in premarket notification submissions in accordance with section 510(k) of the act), recommendations, and other appropriate actions as the Commissioner deems necessary to provide such assurance. For a device that is purported or represented to be for use in supporting or sustaining human life, the Commissioner shall examine and identify the special controls, if any, that are necessary to provide adequate assurance of safety and effectiveness and describe how such controls provide such assurance.
(3) Class III means the class of devices for which premarket approval is or will be required in accordance with section 515 of the act. A device is in class III if insufficient information exists to determine that general controls are sufficient to provide reasonable assurance of its safety and effectiveness or that application of special controls described in paragraph (c)(2) of this section would provide such assurance and if, in addition, the device is life-supporting or life-sustaining, or for a use which is of substantial importance in preventing impairment of human health, or if the device presents a potential unreasonable risk of illness or injury.
[FDA 21CFR860]
[FDA 21CFR807]
[FDA guidance: Reprocessing Medical Devices...(2017)]
[ISO 11139:2018]
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[EU IVDR 2017/746]
— clinical investigation(s) of the device concerned,
— clinical investigation(s) or other studies reported in scientific literature, of a device for which equivalence to the device in question can be demonstrated,
— reports published in peer reviewed scientific literature on other clinical experience of either the device in question or a device for which equivalence to the device in question can be demonstrated,
— clinically relevant information coming from post-market surveillance, in particular the post-market clinical follow-up
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[ISO 13485:2016]
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[EU IVDR 2017/746]
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[FDA 21CFR50, FDA 21CFR56]
Note: The terms research, clinical research, clinical study, study, and clinical investigation are deemed to be synonymous for purposes of this part.
[FDA 21CFR56]
Note: For the purpose of this document, “clinical trial” or “clinical study” are synonymous with “clinical investigation”.
[ISO 14155:2020]
[EU MDR 2017/745]
[EU IVDR 2017/746]
Note: Clinical performance can be defined under national regulations.
[ISO 14155:2020]
Note: In accordance with intended use, clinical performance can include expected values, diagnostic sensitivity and diagnostic specificity based on the known clinical condition or physiological/pathological process/state of the individual, and negative and positive predictive values based on the prevalence of the disease.
[ISO 20916:2019]
[ISO 20916:2019]
(1) A product comprised of two or more regulated components, i.e., drug/device, biologic/device, drug/biologic, or drug/device/biologic, that are physically, chemically, or otherwise combined or mixed and produced as a single entity;
(2) Two or more separate products packaged together in a single package or as a unit and comprised of drug and device products, device and biological products, or biological and drug products;
(3) A drug, device, or biological product packaged separately that according to its investigational plan or proposed labeling is intended for use only with an approved individually specified drug, device, or biological product where both are required to achieve the intended use, indication, or effect and where upon approval of the proposed product the labeling of the approved product would need to be changed, e.g., to reflect a change in intended use, dosage form, strength, route of administration, or significant change in dose; or
(4) Any investigational drug, device, or biological product packaged separately that according to its proposed labeling is for use only with another individually specified investigational drug, device, or biological product where both are required to achieve the intended use, indication, or effect.
[FDA 21CFR3]
Note 1: "Co-packaged combination product" has the meaning set forth in §3.2(e)(2) of this chapter.
Note 2: "Single-entity combination product" has the meaning set forth in §3.2(e)(1) of this chapter.
[FDA 21CFR4]
[ISO 11139:2018]
(1) Internal or interplant transfer of a device between establishments within the same parent, subsidiary, and/or affiliate company;
(2) Any distribution of a device intended for human use which has in effect an approved exemption for investigational use under section 520(g) of the act and part 812 of this chapter;
(3) Any distribution of a device, before the effective date of part 812 of this chapter, that was not introduced or delivered for introduction into interstate commerce for commercial distribution before May 28, 1976, and that is classified into class III under section 513(f) of the act: Provided, That the device is intended solely for investigational use, and under section 501(f)(2)(A) of the act the device is not required to have an approved premarket approval application as provided in section 515 of the act; or
(4) For foreign establishments, the distribution of any device that is neither imported nor offered for import into the United States.
[FDA 21CFR807]
[ISO 13485:2016]
[FDA 21CFR820]
[FDA 21CFR820]
[EU MDR 2017/745, EU IVDR 2017/746]
[EU MDR 2017/745, EU IVDR 2017/746]
Note: Includes contract packagers
[FDA website: Who Must Register...]
[FDA website: Who Must Register...]
Note: The 1976 Copyright Act generally gives the owner of copyright the exclusive right to reproduce the copyrighted work, to prepare derivative works, to distribute copies or phonorecords of the copyrighted work, to perform the copyrighted work publicly, or to display the copyrighted work publicly.
[USPTO]
Note 1: Deviation from instructions for use is only considered use error if it leads to a medical device response that is different than intended by the manufacturer or expected by the user.
Note 2: The figure below shows the relationships of the types of use.
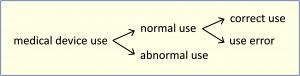
[IEC 62366-1:2015]
[ISO 9000:2015]
[EU MDR 2017/745, EU IVDR 2017/746]
[FDA website: Guide to Inspections of Quality Systems]
[FDA 21CFR812]
Note: However, mass-produced devices which need to be adapted to meet the specific requirements of any professional user and devices which are mass-produced by means of industrial manufacturing processes in accordance with the written prescriptions of any authorised person shall not be considered to be custom-made devices
[EU MDR 2017/745]
Example: Consumer, client, end-user, retailer, receiver of product or service from an internal process, beneficiary and purchaser.
Note: A customer can be internal or external to the organization.
[ISO 9000:2015]
Note 1: It can be that the customer’s expectation is not known to the organization, or even to the customer in question, until the product or service is delivered. It can be necessary for achieving high customer satisfaction to fulfil an expectation of a customer even if it is neither stated nor generally implied or obligatory.
Note 2: Complaints are a common indicator of low customer satisfaction but their absence does not necessarily imply high customer satisfaction.
Note 3: Even when customer requirements have been agreed with the customer and fulfilled, this does not necessarily ensure high customer satisfaction.
[ISO 9000:2015]
Medical device developers are strongly encouraged to consult the listed reference for each key term to fully understand the context behind the definition and its intended application.
Definitions from the FDA Code of Federal Regulation (CFR) are listed without dates and are accurate through December 2020. Consult the listed FDA reference (online) to confirm the latest definition.
